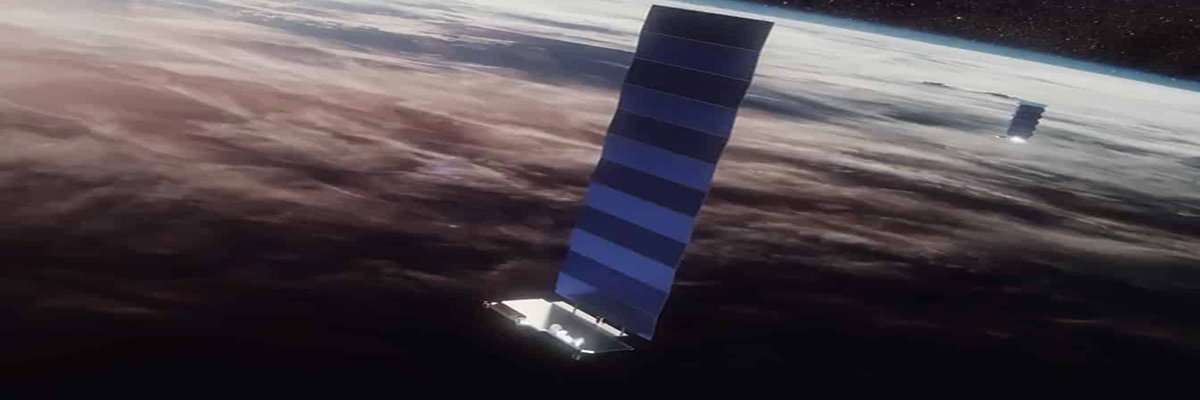
The latest report on the global status of 5G non-terrestrial, networks (NTN) and satellite connectivity from the GSA has revealed that satellite connectivity is moving from niche to mainstream, whether in rural broadband or direct-to-cell use cases, with nearly 200 publicly announced operator–satellite partnerships in almost 100 countries and territories – of these, 34 operators have launched commercial services.
The Non-terrestrial 5G networks and satellite connectivity report from the trade body for the global mobile technology ecosystem drew on publicly available information, focusing on the number of announced mobile network operator and satellite provider partnerships, uses, commercial status, geographic availability and frequency bands being earmarked for NTN use.
The study found that by August 2025, there were 170 publicly announced operator–satellite partnerships in 80 countries and territories, with 34 operators in 25 markets having launched commercial services.
In terms of those driving the provider landscape, it was no surprise to see Starlink as having gained the highest orbit sealing with 44 partnerships, followed by AST SpaceMobile and Lynk.
As an indication of how the Elon Musk-led firm was shaping the market, only weeks ago DE-CIX India said it was making history as the country’s first internet exchange platform to add Starlink to its interconnection ecosystem. In July 2025, Virgin Atlantic announced plans to introduce Starlink in-flight connectivity, offered free of charge for its Flying Club members, creating a digitally connected cabin, across its entire fleet.
As part of its mission to build the first and only space-based cellular broadband network accessible directly by everyday smartphones for commercial and government applications, AST SpaceMobile unveiled in August 2025 plans to expand its space-based communication portfolio. The plan is to send 45 to 60 satellites into orbit by 2026 to support continuous service in the US, Europe, Japan and other strategic markets, including the US government.
In terms of spectrum, the study found that Ka-band remained the most widely used frequency range, supporting both feeder and service links. L- and S-bands were seen as increasingly important for direct-to-cell applications.
Looking at use cases and geography, the report revealed that rural and enterprise broadband remains the dominant application, accounting for half of all partnerships. satellite-to-cell phone services are expanding quickly, with 12 launches and 24 trials or licensed projects, driven by players such as SpaceX, AST SpaceMobile and Lynk, enabling unmodified smartphones to connect in remote areas.
“Today, there are a limited but growing number of smartphones supporting satellite connectivity. Overall, the findings in the GSA’s latest NTN market report point to an evolving landscape where satellite services are moving from niche to mainstream, with strong growth expected in broadband and direct-to-cell offerings, and slower but steady expansion in IoT applications,” said Joe Barrett, president of the global mobile suppliers association.
“From spectrum usage to satellite-operator partnerships, our latest report examines how the satellite connectivity landscape is set to evolve in the rest of 2025 and beyond. And in such a dynamic market, access to this latest data can be critical to business planning and success.”