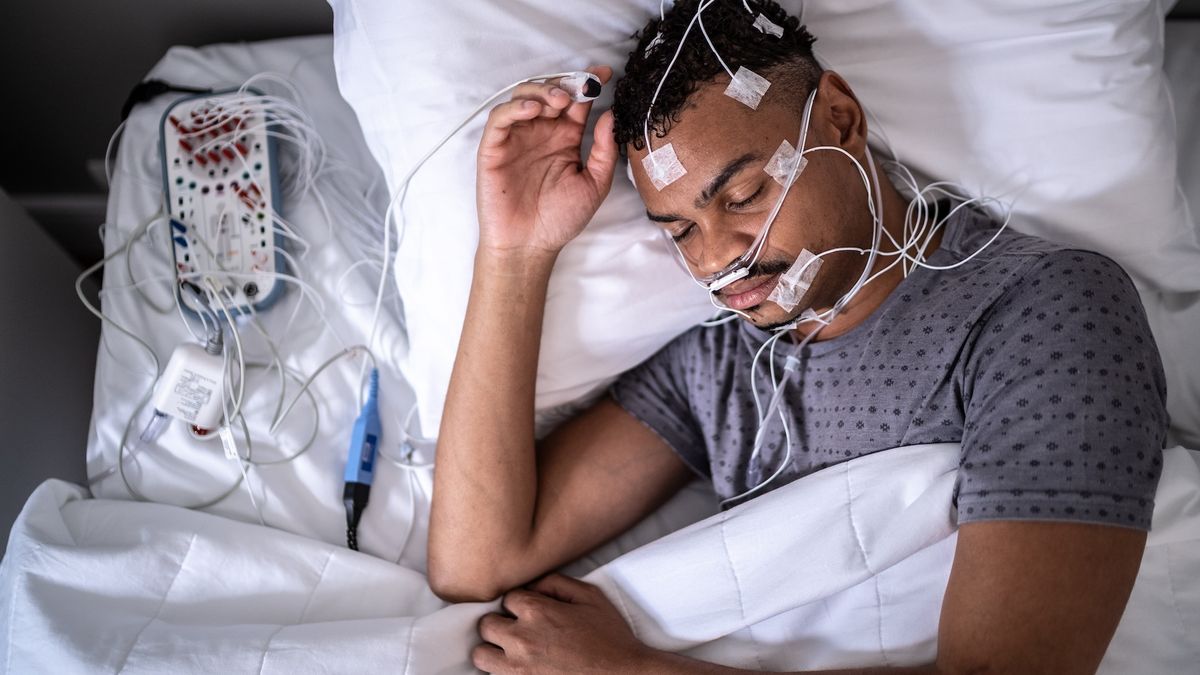
Quick facts about sleep
Sleep Cycles: One rapid eye movement (REM) stage and three non-REM stages that altogether last about 90 to 120 minutes
Benefits: Physical and mental recuperation and memory consolidation
Disorders: Insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, night terrors, restless leg syndrome
By some estimates, the average person spends about one-third of their lives sleeping (or trying to sleep). Sleep is a resting state for the brain and body that occurs at regular intervals, and getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining good health.
When a person is asleep, their core body temperature drops. Heart rate and breathing also slow down and overall metabolic activity decreases by about 10%. A sleeping body may seem inactive at first glance, with the brain relatively unresponsive to external stimuli. But in reality, a sleeping brain is a busy brain. Sleep enables the brain to perform essential repairs and maintenance tasks, building connections between cells that optimize the brain’s performance when awake. Dreaming during sleep is thought to help the brain organize and stabilize memories, as well as process and store information.
Sleep also enables the body to repair and replenish cellular material that is damaged or depleted. Important bodily functions such as the production of hormones, tissue growth and muscle repair, for example, occur mostly while we are asleep, and a system that flushes toxins and waste from the brain is most active in sleep.
Everything you need to know about sleep
What are the stages of sleep?
A normal sleep cycle includes two basic stages known as rapid-eye movement, or REM sleep, and non-REM sleep. In each sleep cycle, there are three stages of non-REM sleep that move the sleeper from light sleep to deeper rest, finally leading to one stage of REM sleep. During a typical period of sleep a person will experience four to six sleep cycles, with each cycle lasting about 90 to 120 minutes. With each successive cycle, the non-REM stages shorten and a greater proportion of the sleeper’s time is spent in REM sleep.
When a person is sleeping, the electrical activity in their brain produces different wave patterns, depending on the stage of their sleep cycle they’re in. These brainwaves vary in frequency, with the waves being more rapid when a person is just starting to fall asleep. The waves then fall into a slower frequency as sleep deepens.
The first part of the sleep cycle is a non-REM stage called N1 that lasts from one to seven minutes. The muscles start to relax, and people are easily woken during this stage of light sleep. This stage is followed by non-REM stages N2 and N3, during which the muscles relax even further as breathing rate and body temperature decrease. The N2 stage lasts about 10 to 25 minutes. The N3 stage, known as deep sleep, lasts around 20 to 40 minutes.
The fourth and final stage, REM sleep, is so named because during this sleep stage the eyes move quickly, though the eyelids remain closed. Muscles other than those that move the eyes become temporarily paralyzed. Most of a person’s dreaming happens during REM sleep. About 25% of time spent asleep is in REM sleep; this stage lasts about 10 minutes but gets longer with every cycle, eventually lasting up to one hour a cycle.
How much sleep does the average person need?
Everyone needs enough sleep, but the overall amount and the length of time spent asleep can vary greatly depending on the person’s age (with additional variations between individuals). Studies suggest that genetics also influence how much sleep a person needs to thrive.
During the first few months of life, newborns typically sleep in stretches that last from 30 minutes to three hours, with about two hours of wakefulness before returning to sleep. Infants from 4 to 12 months old require about 12 to 16 hours of sleep within a 24-hour cycle, including naps throughout the day. At this age, babies still sleep in short stretches but usually start sleeping through the night — about five to six hours uninterrupted — when they are four to six months old. This amount of sleep is critical for the development of babies’ brains and bodies.
Children need more sleep than adults do because they are growing and developing. In order to get enough sleep, young children usually nap during the daytime. Children that are 1 to 2 years old need about 11 to 14 hours of sleep. Between the ages of 3 and 5, children need 10 to 13 hours of sleep every 24 hours, including naps. From ages 6 to 12, a total of nine to 12 hours of sleep is recommended.
Teenagers, who undergo an important developmental growth spurt in their brains and bodies, need at least nine to 9.5 hours of sleep. Puberty also brings shifts in circadian rhythms — roughly 24-hour cycles that bodily functions undergo — and this affects when teens feel sleepy. Compared to kids, teens often find it harder to fall asleep before 11 p.m. and tend to struggle to wake up early in the morning.
On average, adults need about seven to nine hours of uninterrupted sleep each day. As people age, their circadian rhythms shift again. Adults ages 60 and older often go to bed earlier and wake up earlier than younger adults do, and tend to sleep less soundly.
What is insomnia?
Have you ever struggled for hours to fall asleep, woken up much too early or been unable to get back to sleep after awakening in the middle of the night? These bouts of sleep loss are called insomnia. A person with insomnia does not feel refreshed by their fractured or insufficient sleep.
Isolated incidents of lost sleep that span no more than a few days are known as “acute” insomnia. Chronic insomnia, on the other hand, is when you struggle to get sufficient sleep for at least three nights per week, for three months or longer. Insomnia is the most common sleep disorder among people ages 60 and older — and about 10% of people globally experience chronic insomnia at some point during their lifetimes.
Causes of insomnia vary. Insomnia can be driven by stress, physical pain or anxiety. Lack of exercise and excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol or tobacco can also compromise restful sleep. Having an irregular sleep schedule — going to bed at different times or napping during the day — can also trigger insomnia, as can taking medications that increase heart rate or reduce melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep cycles. Genetics, certain medical conditions and certain mental health disorders can also be a factor.
Maintaining a dark and peaceful sleep environment and avoiding habits that can disrupt sleep can help resolve acute insomnia. For chronic insomnia, consulting with a health care professional can help address underlying medical issues that may be disrupting and preventing sleep.
How can sleep deprivation harm your health?
If someone is unable to get the rest that they need, they struggle to function at full capacity, feeling groggy, tired, irritable, uncoordinated or unwell. They may have trouble concentrating or may experience delayed reflexes and muddled memory.
Because sleep deprivation impairs reaction time and responsiveness, it can greatly raise the risk of accidents and injuries. In a study of sleep deprivation in medical residents, who often have highly erratic sleep schedules, cognitive levels in sleep-deprived subjects were comparable to those of people with a blood-alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.05%. To put that into perspective, in the U.S., a driver is considered to be “ability impaired” if their BAC is between .05 and .07%. When people are sleep-deprived, they may also nod off for brief periods, called “microsleeps,” which can be dangerous if they’re operating a vehicle, for instance.
Chronic sleep deprivation can cause what’s known as a “sleep debt.” In the long-term, sleep deprivation carries severe health consequences, affecting the brain as well as various systems in the body, including the cardiovascular, endocrine (hormonal), immune, and nervous systems. Sleep deprivation can worsen existing medical conditions and increase the risk of stroke, Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease. Insufficient sleep can also make people feel hungrier by reducing the production of appetite-suppressing signals while boosting levels of hunger-fueling signals in the body, which may contribute to weight gain in some cases. People who are sleep-deprived are more likely to experience anxiety and depression — that said, both disorders can also cause sleep problems, so the association can go both ways.
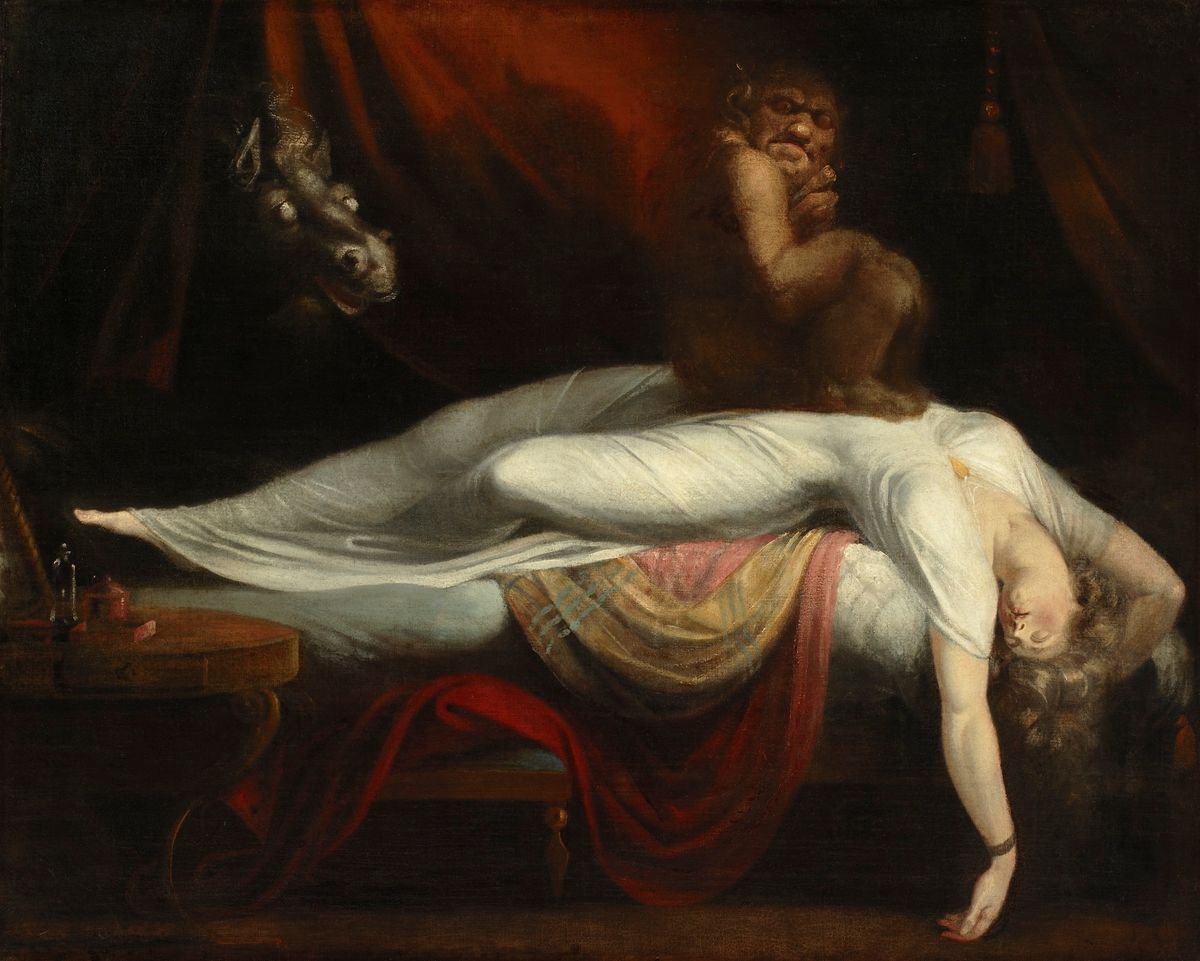

What is “sleep paralysis”?
People don’t usually notice when they transition between sleep and wakefulness. However, sometimes just before falling asleep or waking up, a person may find themselves aware of what is happening around them but unable to speak or move. They may hallucinate, meaning they experience sensations that aren’t actually happening, or feel pressure in their chest. This is a type of sleep disorder, or parasomnia, called sleep paralysis. It’s a temporary state that usually doesn’t last long — typically from a few seconds to a few minutes. In rare cases, though, it can last up to 20 minutes. Regardless of how long the “paralysis” persists, it can be alarming to experience and may affect normal sleep habits by causing anxiety around sleep.
Also called muscle atonia, sleep paralysis happens as a person is entering or leaving REM sleep. During REM, signals from the brain relax muscles in the arms and legs, preventing too much movement during dreaming. In an episode of sleep paralysis, wakefulness occurs while a sleeper’s voluntary muscle control is still offline, causing the person to feel paralyzed.
It’s not clear what causes sleep paralysis, but it has been associated with certain mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Compared to the general public, sleep paralysis is also more common in people with narcolepsy, a condition that causes daytime sleepiness and bouts of sleep that occur suddenly and without warning. Disrupted sleep patterns or the use of certain medications, such as those for treating attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), are also linked to sleep paralysis risk.
Estimates about how common sleep paralysis is vary widely. In one study of more than 400 people in Italy, about 40% reported experiencing sleep paralysis at least once. Other estimates suggest that the number of people worldwide who undergo sleep paralysis at least once in their lifetime is closer to 8%, with women affected slightly more frequently than men.
Sleep glossary
- Circadian rhythm – The internal clock that your body follows during a 24-hour period, moving between alertness and rest in response to changes in light. Circadian rhythms regulate eating habits and other behaviors and bodily functions, in addition to the cycle of sleeping and waking.
- Parasomnia – Disruptive events or behaviors that interfere with restful sleep. These may include sleepwalking, talking during sleep, sleep-related eating disorders, sleep paralysis or intense and vivid nightmares called night terrors.
- Microsleep – A temporary episode of sleep lasting for a few seconds, followed by a swift return to wakefulness. This is sometimes referred to as “nodding off,” and is most likely to occur after sleep deprivation. Microsleeping can be dangerous if it takes place during certain activities, such as driving or operating heavy machinery.
- Sleep debt – The difference between the amount of quality sleep that one requires in order to feel well-rested, and the amount of sleep one actually gets. Accumulated, chronic sleep debt can have lasting health impacts, even after the person “catches up” on their missed sleep.
Sleep pictures
Discover more about sleep
This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice.
Science of sleep quiz: How much do you know about sleep and dreams?