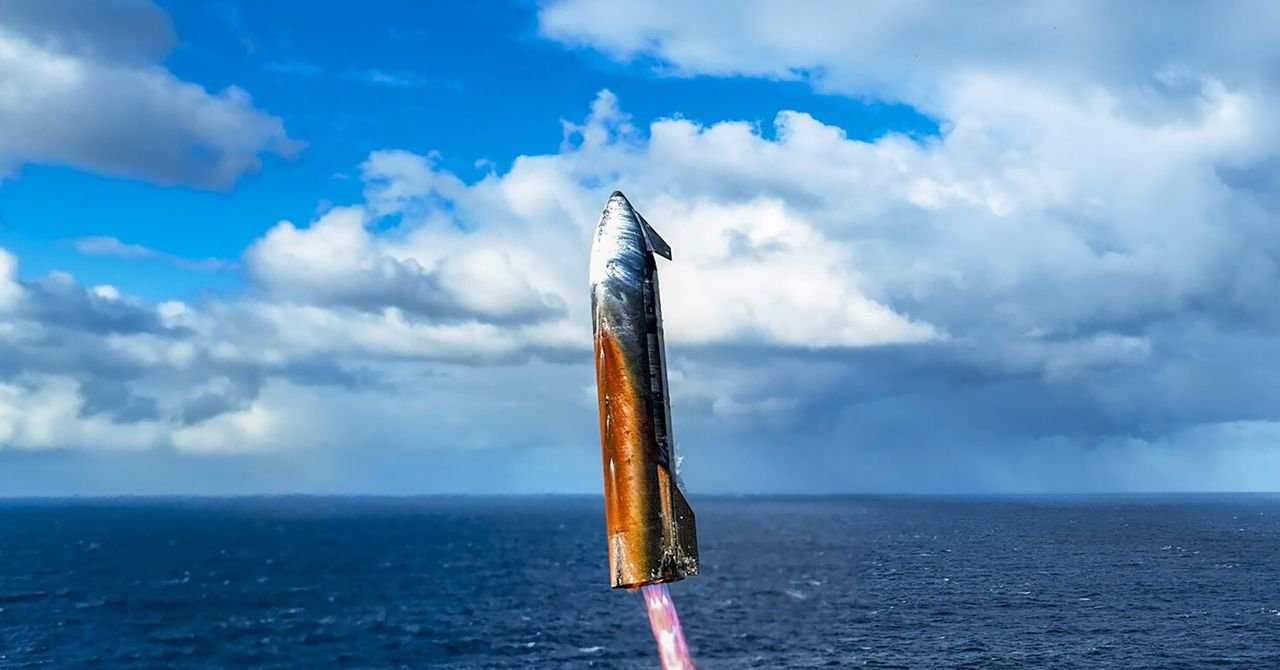
“The metal tiles … didn’t work so well,” he said. “They oxidized extremely nice in the high oxygen environment. So, that nice orange color, kind of like a [space] shuttle external tank color, maybe paying homage to the shuttle program, was created by those three little metal tiles up on top.”
Gerstenmaier has a talent for explaining complex technical concepts in a digestible manner. He began his career as an aerospace engineer working on the space shuttle program at NASA in 1977. He rose through the ranks at NASA to become head of all of the agency’s human spaceflight programs, then joined SpaceX in 2020.
The experiment with metallic tiles is emblematic of the way SpaceX is developing Starship. The company’s engineers move quickly to make changes and integrate new designs into each test flight. Metallic heat shield tiles aren’t a new technology. NASA tested them in labs in the 1970s but never flew them.
“I think we learned a lot by taking them to flight, and we still had enough protection underneath that they didn’t cause a problem,” Gerstenmaier said. “In most of the tiles, there are fairly large gaps, and that’s where we’re seeing the heat get through and get underneath.”
A mastery of Starship’s heat shield is vital for the future of the program. The heat shield must be durable for Starship to be rapidly reusable. Musk eyes reflying Starships within 24 hours.
NASA’s reusable space shuttles used approximately 24,000 delicate ceramic tiles to protect them from the hottest temperatures of reentry, but the materials were delicate and damage-prone, requiring refurbishment and touchups by hand between missions. SpaceX’s Dragon crew capsule has a reusable structure that underlies the heat shield, but the heat shield material itself is only used once.
For Starship, SpaceX needs a heat shield that will stand up to the rigors of spaceflight—intense vibrations during launch, extreme thermal cycles in space, the scorching heat of reentry, and the crush of the launch pad’s catch arms at the end of each mission. Musk has called the ship’s reusable heat shield the “single biggest” engineering challenge for the Starship program.
Continuing his presentation, Gerstenmaier pointed to a patch of white near the top of Starship’s heat shield. This, he said, was caused by heat seeping between gaps in the tiles and eroding the underlying material, a thermal barrier derived from the heat shield on SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft. Technicians also intentionally removed some tiles near Starship’s nose to test the vehicle’s response.
“It’s essentially a white material that sits on Dragon, and it ablates away, and when it ablates it creates this white residue,” Gerstenmaier said. “So what that’s showing us is that we’re having heat essentially get into that region between the tiles, go underneath the tiles, and this ablative structure is then ablating underneath. So we learned that we need to seal the tiles.”
The primary structure for Starship is made of a special alloy of stainless steel. Most other spacecraft designed for reentry, like the space shuttle and Dragon, are made of aluminum. The steel’s higher melting point makes Starship more forgiving of heat shield damage than the shuttle.